Indus Water Treaty Explained | India-Pakistan River Agreement
What is the Indus Water Treaty?
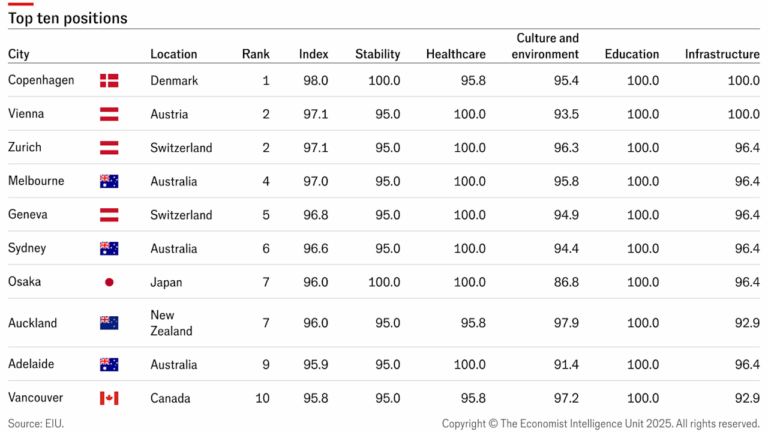
The Indus Water Treaty (IWT) is a water-distribution treaty between India and Pakistan, brokered by the World Bank and signed in 1960. The treaty establishes a mechanism to manage and share the waters of the Indus River and its tributaries, fostering cooperation between the two nations.
Why is the Indus Water Treaty in News?
Recently, the Indus Water Treaty has been a subject of renewed scrutiny due to geopolitical tensions and climate change impacts. Both nations have engaged in diplomatic discussions to address emerging challenges and concerns over water resource management.
The History of the Indus Water Treaty
The roots of the treaty trace back to the partition of British India in 1947, which left the control of water resources between the two newly formed states contentious. The intervention by the World Bank led to the signing of the treaty on September 19, 1960, by then Indian Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru and Pakistani President Ayub Khan.
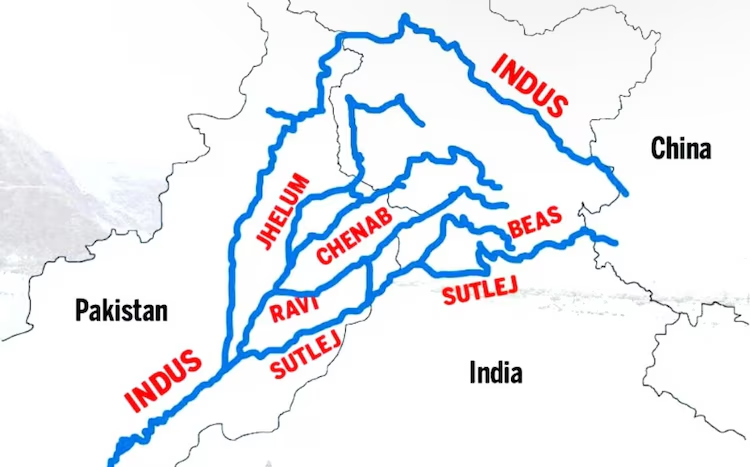
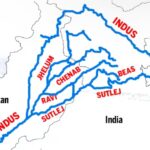
Indus River and Its Tributaries
The Indus River system comprises two main parts:
- Western Rivers:
- Indus River
- Jhelum River
- Chenab River
- Eastern Rivers:
- Sutlej River
- Beas River
- Ravi River
Under the treaty, India has control over the eastern rivers, while Pakistan has rights over the western rivers with limited usage rights for India.
Important Facts about the Indus Water Treaty
- The treaty allocates about 20% of the Indus waters to India and the remaining 80% to Pakistan.
- It is one of the few successful international treaties that has survived multiple wars between the nations.
- The treaty allows India to use the western rivers for limited irrigation, transport, and power generation.
Various Projects Under IWT
- Baglihar Dam: This project on the Chenab River led to significant discussions between the two countries.
- Kishanganga Hydroelectric Plant: Situated on the Jhelum River, it sparked debates regarding water flow and utilization.
- Sutlej River Projects: Various hydroelectric projects that focus on the sustainable utilization of eastern river rights.
UPSC Prelims PYQs on Indus Water Treaty
- Which of the following rivers is NOT a part of the Indus Water Treaty?
- A) JhelumB) SutlejC) YamunaD) Ravi
- The Indus Water Treaty was brokered by which international organization?
- A) United Nations
- B) International Monetary Fund
- C) World Bank
- D) Asian Development Bank
UPSC Mains Questions on Indus Water Treaty
- Discuss the significance of the Indus Water Treaty in managing water resources between India and Pakistan. What are the challenges and opportunities presented by this treaty?
- Analyze the impact of climate change on the Indus River and its tributaries as outlined in the Indus Water Treaty. What adaptations should India and Pakistan consider to address these changes?
Also Read : Pakistan Suspends Simla Agreement